1. Introduction: The New Cybersecurity Reality
• Cyberattacks have shifted from large enterprises to small and mid‑sized businesses.
• Insurance agencies and professional service firms are now high‑value targets.
• Brief explanation of why attackers prefer smaller organizations today.
2. Why Small Businesses Are Being Targeted
• Lower security budgets and fewer dedicated IT staff.
• Increased reliance on cloud services and remote work.
• Attackers automate scanning for vulnerabilities — size no longer matters.
• Insurance agencies hold sensitive personal data, making them especially attractive.
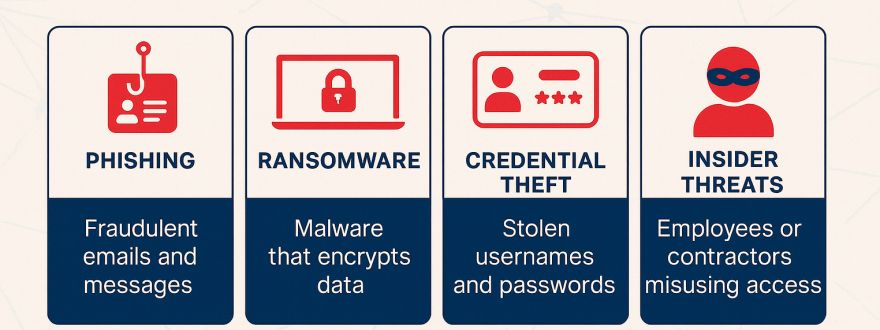
3. The Most Common Threats in 2026
• Phishing & Business Email Compromise (BEC)
Still the #1 attack vector; now more sophisticated with AI‑generated emails.
• Ransomware
Targeting backups, cloud storage, and remote access systems.
• Credential Theft & MFA Fatigue Attacks
Attackers trick users into approving MFA prompts.
• Supply Chain & Vendor Breaches
Small businesses inherit risk from software and service providers.
4. Why Traditional Security Is No Longer Enough
• Antivirus alone cannot stop modern threats.
• Firewalls don’t protect remote workers or cloud apps.
• Passwords are the weakest link in most organizations.
• Attackers now use automation and AI to scale attacks.
5. The Shift Toward Modern Cybersecurity Practices
Introduce educational concepts such as:
• Zero Trust (“never trust, always verify”)
• Least Privilege Access
• Multi‑Factor Authentication (MFA)
• Endpoint Detection & Response (EDR)
• Security Awareness Training
• Backup & Recovery Testing
Explain each in simple, non‑technical terms.
6. Real‑World Impact on Small Businesses
• Average downtime after a ransomware attack.
• Cost of recovery vs. cost of prevention.
• Insurance implications — cyber liability carriers now require stronger controls.
• Reputational damage and client trust issues.
7. What Businesses Can Do Today (Educational, Not Salesy)
Provide practical, actionable steps:
• Enable MFA everywhere.
• Train staff to spot phishing.
• Keep systems patched.
• Use modern endpoint protection.
• Review backup strategy and test restores.
• Audit user access and permissions.
These are universal best practices — no sales pitch needed.
8. Conclusion: Cybersecurity Is Now a Business Priority
• Cybersecurity is no longer optional or “just an IT issue.”
• Small businesses that take proactive steps dramatically reduce their risk.
• A reminder that awareness and education are the first line of defense.




